Object Storage is a storage model that answers the IT need to manage lots of data — cross-platform and with performance.
For a long time, we used heavy databases with table structures and well-organized records. Then, the advent of information technology in many fields has increased the need to store and manage unstructured data cross-platform with performance, like high-quality medical images, Netflix movies, and more.
They occupy many GBs and TBs, making up a large part of the data we manage today. This cannot be organized in a database but with an Object Storage system. Object Storage has access equal to 1: I know the object’s name (i.e., the key), and I get the value. And it can scale infinitely without increasing the waiting time or the need to reorganize a file system.
Last point: nowadays, more and more Object Storage systems provide S3 compatibility, allowing integrations with services based on the AWS S3 standard.
Related reading: What is Object Storage? Use cases & advantages
Object Storage vs File Storage vs Block Storage: What's the Difference?
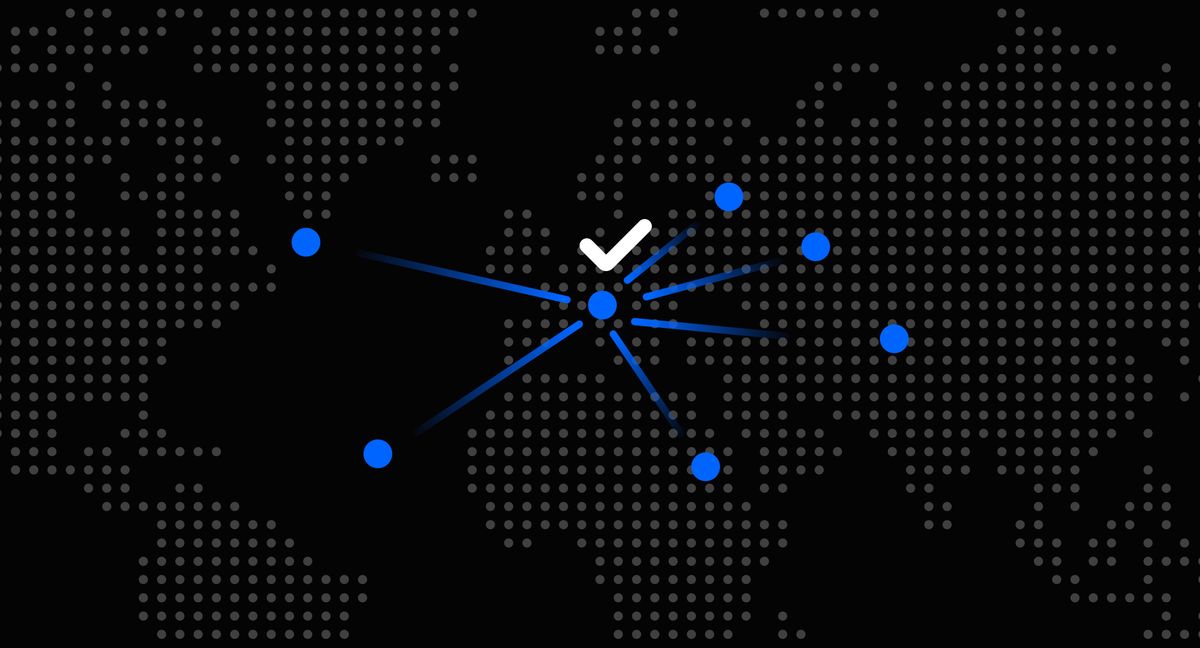
Object Storage identifies each data set as a single unit known as an 'object.' It contrasts with the much more common file storage, in which data is managed as files in a hierarchical structure and identified by their location on disk, and block storage, in which data are collected as blocks structured in sequences that are non-hierarchical sequences of bytes.
What makes Object Storage unique is that objects contain not only raw data but also metadata and a globally unique identifier (ID). This expedient allows timely indexing, which facilitates the work of the system administrator: it’s no longer necessary to worry about details such as the path to a file or the hardware on which the data is stored since everything is abstracted in the form of objects. The use of metadata means that a theoretically infinite number of objects is buildable with no size limit, simplifying data migration and classification. Storage can scale seamlessly over large data sets in multi-node and multi-site systems.
Related reading: What is a hybrid cloud model? Examples and benefits in 2023
This versatility makes data programmable, enabling features not guaranteed by file and block storage, such as granular management of data distribution and replication. Thus, if block storage can be compared to a parking lot and file storage to a multi-story parking lot, Object Storage can be compared to a valet. That is, to an intelligent agent that can quickly retrieve any data effortlessly.
What are the benefits of Cubbit’s Object Storage?
Cubbit is a geo-distributed Object Storage that’s secure, S3 compatible, and immutable.
In Cubbit, each user is one or more nodes of the network. Each stored data is encrypted with AES-256, micro-fragmented, and geo-distributed in multiple copies in a p2p network under user control.
The service is s3 compatible and supports S3 Object Locking, Object Versioning, and S3 Multipart Upload. The UX is simple: you can switch from AWS to Cubbit by changing one configuration parameter in the CLI.
Want to see Cubbt in action? Look at our latest demo >